Climate Change
Home / Climate Change
Every day, engineers are leading the way to build a greener and more environmentally sustainable energy future.
Last fall, IEEE PES commissioned a nationwide survey to gauge the public’s perception of climate change, and specifically the role of engineers in driving solutions to combat climate change.
The results indicate that:
Believe engineers play an important role in environmental protection
Agree that engineers are leaders in the fight against climate change
Feel confident that engineers can develop solutions to help address climate change
Source: Park Street Stategies Survey, commissioned by IEEE PES, November 2023.
View the full survey results here. [PDF 1.7MB]
IEEE PES can and should be more vocal about the innovative work engineers are doing to progress climate solutions.
Some Key Takeaways
- 72% view an outdated electric grid presents the biggest energy-related challenge, followed by government mandates and net-zero goals being misaligned with the current energy infrastructure realities.
- 50% worry that it may be difficult to reverse climate change on a global scale but 60% believe that technology is the key to addressing it.
- More than a third has little understanding of the role that engineers play in addressing climate change.
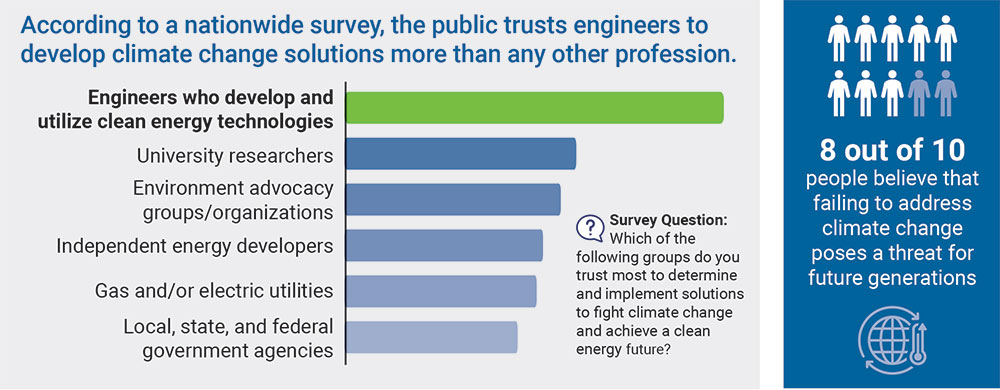
- Even so, respondents trust engineers the most to find solutions to achieving a clean energy future, more so than researchers, environmental advocacy groups, utility companies, or government agencies.
- 79% believe that engineers have the knowledge and skill set to research and develop new forms of renewables.
What does that mean for IEEE and PES?
- Most respondents view engineers positively and acknowledge that they play a key role in addressing climate change, but do not understand what that role is. Educating the public about their role would be beneficial.
- A large majority – 82% – expressed an interest in learning more about what engineers are doing, or planning to do, to address climate change.
- Messages that provide concrete examples of what engineers do to address climate change (e.g., constructing green buildings, monitoring environmental conditions, reducing electronic waste, etc.) resonate the most.
- Engineers are most often described with positive terms such as “innovative,” “creative,” and “smart.”
When it comes to describing our energy future, the word “sustainable” resonates the most, followed by “cleaner.” Words like “smart,” “modernized,” and “engineered” resonate less.
Other IEEE Climate Change Resources
Every day, engineers are leading the way to build a greener and more environmentally sustainable energy future.
Last fall, IEEE PES commissioned a nationwide survey to gauge the public’s perception of climate change, and specifically the role of engineers in driving solutions to combat climate change.
The results indicate that:

Climate change and extreme weather are top environmental concerns nationwide.
A majority are optimistic that technology is the key to addressing our climate future.
Believe engineers play an important role in environmental protection
Agree that engineers are leaders in the fight against climate change
Feel confident that engineers can develop solutions to help address climate change
View the full survey results here. [PDF 1.7MB]
IEEE PES can and should be more vocal about the innovative work engineers are doing to progress climate solutions.
Some Key Takeaways
- 72% view an outdated electric grid presents the biggest energy-related challenge, followed by government mandates
and net-zero goals being misaligned with the current energy infrastructure
realities. - 50% worry that it may be difficult to reverse climate change on a global scale but 60% believe that technology is the key to addressing it.
- More than a third has little understanding of the role that engineers play in addressing climate change.
- Even so, respondents trust engineers the most to find solutions to achieving a clean energy future, more so than researchers, environmental advocacy groups, utility companies, or government agencies.
- 79% believe that engineers have the knowledge and skill set to research and develop new forms of renewables.
What does that mean for IEEE and PES?
- Most respondents view engineers positively and acknowledge
that they play a key role in addressing climate change, but do not
understand what that role is. Educating the public about their role would
be beneficial. - A large majority – 82% – expressed an interest in learning more about what engineers are doing, or planning to do, to address climate change.
- Messages that provide concrete examples of what engineers do to address climate change (e.g., constructing green buildings, monitoring environmental conditions, reducing electronic waste, etc.) resonate the most.
- Engineers are most often described with positive terms such as “innovative,” “creative,” and “smart.”
When it comes to describing our energy future, the word “sustainable” resonates the most, followed by “cleaner.” Words like “smart,” “modernized,” and “engineered” resonate less.
IEEE PES Perspectives
Our members have made climate change initiatives a priority. Read what they have to say about power and energy, and how we can make a difference through the smart applications of technology.
- All
- Aerospace electronics
- Aging
- Air pollution
- Aircraft propulsion
- Airplanes
- Array signal processing
- Authentication
- Automotive engineering
- Batteries
- Bayes methods
- Biological system modeling
- Biomass
- Boats
- Carbon
- Carbon dioxide
- Carbon emissions
- Carbon tax
- Caron emissions
- Circuit breakers
- Circuit faults
- Climate change
- Coal
- Cogeneration
- Computational modeling
- Computer architecture
- Conference Panel
- Control systems
- Controllability
- Convex functions
- Cooling
- Correlation
- Costs
- Cryogenics
- Current transformers
- Data models
- Data processing
- Decarbonization
- Decision making
- Decision theory
- Deep learning
- Degradation
- Dielectric breakdown
- Digital simulation
- Discharges (electric)
- Distributed databases
- Economics
- Electric breakdown
- Electric potential
- Electric vehicles
- electricity
- Electricity supply industry
- Electrodes
- Emissions trading
- Energy consumption
- Energy efficiency
- Energy management
- Energy measurement
- Energy resolution
- energy saving
- Energy storage
- Energy Transportation
- Environmental factors
- Europe
- Feature extraction
- Feedback loop
- Finance
- Fires
- Floods
- Forecasting
- Fossil fuels
- foundational support systems
- Frequency control
- Frequency conversion
- Frequency measurement
- Fuel cells
- Fuels
- Gases
- General Meeting
- Generators
- Geology
- Global warming
- Government policies
- green
- Green products
- Greenhouse effect
- Grid Technologies
- Harmonic analysis
- Heat pumps
- Heating
- Heating systems
- Hurricanes
- HVDC transmission
- Hybrid power systems
- Hydrogen
- Hydrogen powered vehicles
- Hydrogen storage
- Ice
- IEEE smart grid
- Insulation
- Intelligent sensors
- Internal combustion engines
- interview
- Inverters
- Investment
- Investments
- ISGT
- Islanding
- Levee
- lifestyles
- Lighting
- Load flow analysis
- Load management
- Load modeling
- Low-carbon economy
- Maintenance engineering
- Markov processes
- Mathematical model
- Measurement
- Meteorological factors
- Meteorology
- Microgrids
- new information technologies
- Open source software
- Optimization
- Panel Discussion
- Partial discharges
- PES Day
- Photovoltaic systems
- Planning
- Power distribution planning
- Power electronics
- Power generation
- Power grid
- Power grids
- Power markets
- Power outages
- Power system dynamics
- Power system economics
- Power system planning
- Power system reliability
- Power system stability
- Power systems
- Power transmission
- Power transmission lines
- Predictive models
- Pricing
- Probabilistic logic
- Probability density function
- Production
- Programming
- Protons
- Reactive power
- Real-time systems
- Regulation
- Reinforcement learning
- reliability
- Renewable energy sources
- Renewal Energy
- Resilience
- Resistance heating
- Resource management
- Risk management
- Robustness
- Routing
- Runtime
- Safety
- Satellites
- Sea measurements
- Security
- Sensor systems and applications
- Smart Buildings
- Smart cities
- Smart grids
- Solar energy
- Solar panels
- Solar power generation
- Space heating
- Stakeholders
- Statistics
- Stochastic processes
- Storms
- Sulfur hexafluoride
- Superconductivity
- Support vector machines
- Sustainable development
- Switchgear
- System integration
- TandD
- Target recognition
- TD Grid Modernization
- Technical Report
- Technological innovation
- Thermostats
- Transactive energy
- Transforms
- Transient analysis
- Transportation
- Trigeneration
- Tropical cyclones
- Uncertainty
- Urban areas
- Value of DERs
- Value of Grid Resources
- Video
- Voltage control
- Voltage fluctuations
- Voltage measurement
- Waste management
- Water heating
- Water resources
- Webinar
- Wind
- Wind energy
- Wind energy generation
- Wind farms
- Wind forecasting
- Wind power generation
- Wind turbines
- Wireless communication
ComEd Grid Labs-Why the Power Sector Needs Advanced Labs
Operational Security in 100% Inverter-Based Power Systems: Experiences from Hawai‘i
Read More >
Hydrogen-Powered Aircraft: Hydrogen-Electric Hybrid Propulsion for Aviation
Read More >
Strengthening Transmission System Resilience Against Extreme Weather Events by Undergrounding Selected Lines
Read More >
Lighting a Reliable Path to 100% Clean Electricity: Evolving Resource Adequacy Practices for a Decarbonizing Grid
Read More >
Mobile and Portable De-Icing Devices for Enhancing the Distribution System Resilience Against Ice Storms: Preventive Strategies for Damage Control
Read More >
Utility-Scale Shared Energy Storage: Business Models for Utility-Scale Shared Energy Storage Systems and Customer Participation
Read More >
Multi-Energy Microgrids: Designing, Operation Under New Business Models, and Engineering Practices in China
Read More >
Data-Driven Classifier for Extreme Outage Prediction Based On Bayes Decision Theory
Read More >
Enable a Carbon Efficient Power Grid via Minimal Uplift Payments
Read More >
Islanding Detection of Grid-Forming Inverters: Mechanism, Methods, and Challenges
Read More >
Intra-Hour Photovoltaic Generation Forecasting Based on Multi-Source Data and Deep Learning Methods
Read More >
Flexibility in Sustainable Electricity Systems: Multivector and Multisector Nexus Perspectives
Read More >
The Fragile Grid: The Physics and Economics of Security Services in Low-Carbon Power Systems
Read More >
Latin American Energy Markets: Investment Opportunities in Nonconventional Renewables
Read More >
Supporting Energy Transition in Transmission Systems: An Operator’s Experience Using Electromagnetic Transient Simulation
Read More >
A Numerical Approach for Hybrid Simulation of Power System Dynamics Considering Extreme Icing Events
Read More >
Planning With Multiple Transmission and Storage Investment Options Under Uncertainty: A Nested Decomposition Approach
Read More >
A Probabilistic Transmission Planning Framework for Reducing Network Vulnerability to Extreme Events
Read More >
Robust Resiliency-Oriented Operation of Active Distribution Networks Considering Windstorms
Read More >
From Reliability to Resilience: Planning the Grid Against the Extremes
Read More >
A Multi-State Model for Transmission System Resilience Enhancement Against Short-Circuit Faults Caused by Extreme Weather Events
Read More >
Stochastic Unit Commitment in Isolated Systems With Renewable Penetration Under CVaR Assessment
Read More >
Resilience Enhancement With Sequentially Proactive Operation Strategies
Read More >
Other IEEE Climate Change Resources
© Copyright 2023 IEEE — All rights reserved. A not-for-profit organization, IEEE is the world’s largest technical professional organization dedicated to advancing technology for the benefit of humanity.







